Factors Affecting Blood Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: The Role of Diet, Physical Activity, and Medication Adherence in The Prolanis Program at Denkesyah Clinic, Madiun, East Java
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16996039Keywords:
Blood glucose levels, Diet, Medication adherence, Physical activity, ProlanisAbstract
Background: Diabetes Mellitus (DM) is a chronic disease that requires continuous management. Blood glucose control is strongly influenced by lifestyle factors, including diet, physical activity, and medication adherence. This study aimed to analyze the effect of diet, physical activity, and medication adherence on blood glucose levels among diabetes mellitus patients participating in the Prolanis program at Denkesyah Clinic, Madiun, East Java. Methods: A quantitative cross-sectional study at Denkesyah Clinic Madiun, from June to July 2025. A total of 69 respondents were purposively selected from 224 Prolanis participants. Data were collected using structured questionnaires and fasting blood glucose measurements. Multiple linear regression analysis was applied to determine the associations between variables. Results: Diet was categorized as good (37.7%), physical activity as moderate (34.8%), medication adherence as high (43.5%), and blood glucose as abnormal (50.7%). Regression analysis revealed significant associations between diet (p=0.030), physical activity (p=0.001), and medication adherence (p=0.000) with blood glucose. Medication adherence was the most influential factor (highest Beta). Conclusions: Diet, physical activity, and medication adherence significantly affect blood glucose control, with adherence to medication being the strongest determinant. Strengthening education and adherence monitoring within the Prolanis program is essential for achieving optimal glycemic control.
Downloads
References
Ardiani, H. E., Permatasari, T. A. E., & Sugiatmi, S. (2021). Obesity, dietary patterns, and physical activity in managing diabetes mellitus during the COVID-19 pandemic. Muhammadiyah Journal of Nutrition and Food Science (MJNF), 2(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.24853/mjnf.2.1.1-12
International Diabetes Federation. (2022). Diabetes around the world in 2021. Retrieved June 2, 2025, from https://diabetesatlas.org/
International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas. Retrieved June 2, 2025, from https://www.diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/94/id.html
Jilao, M. (2017). The level of adherence to the use of oral antidiabetic drugs in diabetes mellitus patients at Koh-Libon Health Center, Thailand. [Undergraduate Thesis, Maulana Malik Ibrahim State Islamic University, Malang].
Kristiawan, P. A., Nugroho, R., Maria, R. R., & Noviani, T. (2019). Dietary patterns as a cause of non-communicable diseases (diabetes mellitus, obesity, and hypertension) in the working area of Cebongan Health Center, Salatiga City. Jurnal Kesehatan. Retrieved from ukh.ac.id/index.php/JK/article/view/324/274
Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia. (2020). Infodatin 2020: Diabetes Mellitus. Jakarta: Data and Information Center, Ministry of Health RI.
Loghmani, E. (2018). Guidelines for adolescent nutrition services: Chapter 14. Diabetes Mellitus: Type 1 and Type 2. School of Public Health.
Pratita, N. D. (2017). The relationship between partner support, health locus of control, and treatment adherence in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Scientific Journal of Students, University of Surabaya.
Sartika. (2013). The relationship between dietary patterns and type 2 diabetes mellitus at the Internal Medicine Clinic, Prof. Dr. R. D. Kandou Hospital Manado. E-Journal Keperawatan (E-Kp), 1(1).
Saryono, & Anggraeni, M. D. (2013). Quantitative and qualitative research methods in health sciences (1st ed.). Nuha Medika.
Setyawan, S., & Sono. (2015). The relationship between physical activity and random blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus patients. Jurnal Keperawatan, 11(1), 127–130.
Soelistijo, S. A., Lindarto, D., Decroli, E., Permana, H., Sucipto, K. W., Kusnaidi, Y., & Budiman. (2019). Guidelines for the management and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults in Indonesia (1st ed.). PB Perkeni.
Suprapti, D. (2017). The relationship between carbohydrate, protein, and fat intake and diabetes mellitus in the elderly. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 21(2), 1689–1699.
Suryati, I. (2021). Effective nursing exercises for diabetes mellitus patients based on research findings (1st ed.). Deepublish Publisher.
Susanti, S., & Bistara, D. N. (2018). The relationship between dietary patterns and blood glucose levels in diabetes mellitus patients. Jurnal Kesehatan Vokasional, 3(1).
Sw, W. N. U. N., Zaetun, S., & Khusuma, A. (2019). The role of nutrition in preventing non-communicable diseases. Jurnal Analis Medika Bio Sains, 6(1), 1–7.
Tadra, H. (2017). Everything you need to know about diabetes (2nd ed.). PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Tjokroprawiro, A., & Murtiwi, S. (2014). Non-pharmacological therapy for diabetes mellitus. In S. Setiati, I. Alwi, A. W. Sudoyo, M. Simadibrata, B. Setiyohadi, & A. F. Syam (Eds.), Textbook of internal medicine (Vol. 2, 6th ed.). Jakarta: Interna Publishing.
Tjekyan, R. (2010). Incidence and factors of type 2 diabetes mellitus in 78 neighborhoods in Palembang Municipality. Jurnal Kedokteran dan Kesehatan, 2, 88.
Widiyanto, J., & Rahayu, S. (2019). The effect of dietary patterns on the incidence of diabetes mellitus at Sidomulyo Inpatient Health Center, Pekanbaru City. Proceedings of SainsTeKes National Seminar, MIPAKes UMRi, 1, 1–7.
World Health Organization. (2016). Global report on adult learning: Executive summary. WHO.
Yulianto, S. (2014). Dangerous foods for diabetes (3rd ed.). Rineka Cipta.
Zamora-Kapoor, A., Fyfe-Johnson, A., Omidpanah, A., Buchwald, D., & Sinclair, K. (2018). Risk factors for pre-diabetes and diabetes in adolescence and their variability by race and ethnicity. Preventive Medicine, 115, 47–52.
More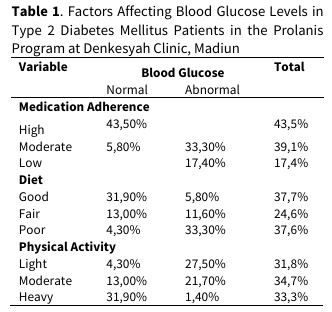
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Sad Omega Kencanawaty, Nurwijayanti, Novita Ana Anggraini (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

