Implementation of Puskesmas Pregnancy and Complication Prevention Program (P4K) as Implementation of SDGs at Healthcare Facilities: a Systematic Literature Review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.15307977Keywords:
Birth Planning and Complication Prevention, P4K, AKI, Community Health Center, SDGsAbstract
Background: Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR) remains a global issue wich is in line with the third SDGs, Indonesia having the third highest MMR in ASEAN at 189 per 100,000 live births. To reduce MMR, Indonesia implements the Childbirth Planning and Complication Prevention Program (P4K), but there are still many shortcomings that require further study on the factors affecting its implementation. Methods: The research method uses a Systematic Literature Review. Journal search terms are formulated using the PICO(S) framework. The literature search in this study used two databases, namely the National Library and Google Scholar. Results: The research results showed that 7 out of 10 articles explained that the successful implementation of the program was caused by the communication skills of midwives as health service providers, human resources, budget, dispositions and policies, bureaucracy and standard operational procedures, facilities and infrastructure. Meanwhile, the 3 articles explained stated that the success of the program was caused by the knowledge, attitudes and family support of pregnant women. Conclusions: The program's success is mainly attributed to factors like midwives' communication skills, resources, budget, policies, and infrastructure, while a smaller focus is placed on the knowledge, attitudes, and family support of pregnant women.
Downloads
References
ASEAN Secretariat. (2020). Data Angka Kematian Ibu di ASEAN. ASEAN Secretariat
Herlina, S. M., Zulviana, Y., & Ulya, Y. (2021). Peran Bidan terhadap Pelaksanaan Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K) dalam Menurunkan Angka Kematian Ibu. Jurnal Kesehatan Masyarakat Vol. 7 No. 2 .
Himalaya, D., & Maryani, D. (2020). Penerapan Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K). Journal of Midfifery Vol. 8 No. 1.
Insiyah, N. S., & Indrawati, F. (2021). Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi di Puskesmas. Indonesian Journal of Public Health and Nutrition.
Kemenkes RI. (2009). Pedoman Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan PEncegahan Komplikasi dengan Stiker. Jakarta: Kementerian Kesehatan RI.
Kemenkes RI. (2022). Profil Kesehatan Indonesia 2021. Jakarta: Kementerian
Kesehatan RI. Kementerian PPN/Bappenas. (2020). Pedoman Teknis Penyusunan Rencana Aksi Tujuan Pembangunan Berkelanjutan (TPB)/Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Jakarta: Kementerian PPN/Bappenas.
Khoeroh, H. (2019). Evaluasi Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K) sebagai Upaya Menurunkan Angka Kematian Ibu di Puskesmas Paguyangan Kab. Brebes Tahun 2018. Jurnal Kesehatan Ilmiah Indonesia Vol. 4 No. 2.
Marapung, R. A., & Kumalasari. (2020). Gambaran Pelaksanaan Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikaso (P4K) pada Ibu Hamil di Masa Pandemi Covid-19 di Puskesmas Namorambe Kabupaten Deli Serdang Tahun 2021. Jurnal Kebidanan Medan
MArdiah, & Hardiana, H. (2018). Alternatif Kebijakan Operasional Audit Maternal Perinatal (AMP) Di Kabupaten Barito Kuala Kalimantan Selatan. Jurkessia Vol. 8 No. 2 .
Patimah, S., Trianty, T., & Kurnia, H. (2021). Pengaruh Komunikasi dan Sumber Daya Terhadap Capaian Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi. Journal of Midwifery Information Vol. 1 No. 2.
Prajayanti, H., Maslikhah, & Baroroh, I. (2019). Implementasi Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K) di Puskesmas PONED Kabupaten Pekalongan. Jurnal Kebidanan Harapan Ibu Pekalongan (Vol 6 No. 2.)
Purwaningrum, Y., & Restanty, D. A. (2020). Penerapan Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi (P4K) oleh Bidan di Kabupaten Jember. Mimbat Ilmiah esehatan Ibu dan Anak.
Rahmawati, A., & Wulandari, R. (2019). Influence of Physical and Psychological of Pregnant Women Toward Health Status of Mother and Baby. Jurnal Kebidanan Vol. 9 No. 2.
Siswari, B. D., & Aprianti, N. A. (2020). Hubungan Kualitas KIE Bidan saat P4K (Program Perencanaan Persalinan dan Pencegahan Komplikasi) dengan Persiapan Ibu Hamil dalam Perencanaan Persalinan di Puskesmas Masbagik. Prohealth Journal Vol. 17 No. 1.
WHO. (2023, Februari 22). World Health Organization: Maternal Mortality. Retrieved from World Health Organization: Maternal Mortality: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/maternal- mortality
Yasril, A. I., & Rahmadani, W. (2019). Faktor yang Berhubungan tentang P4K dengan Kesiapan Persalinan di Kelurahan Parupuk Tabing. Jurnal Human Care.
More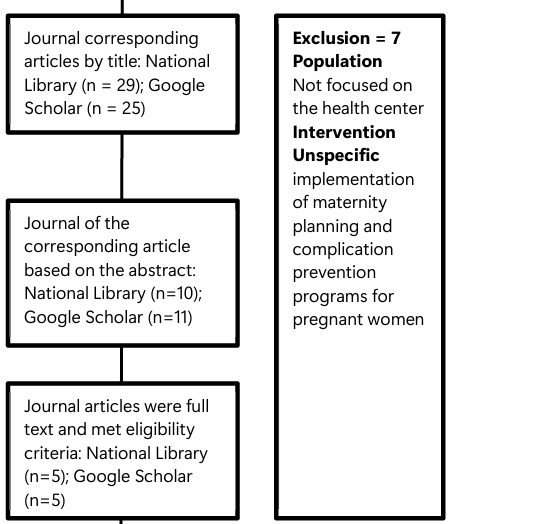
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Dewi Rokhmah, Tasya Lukita Cyndi Pradana, Heruddin, Nur Aziza Wahdaliya (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.

